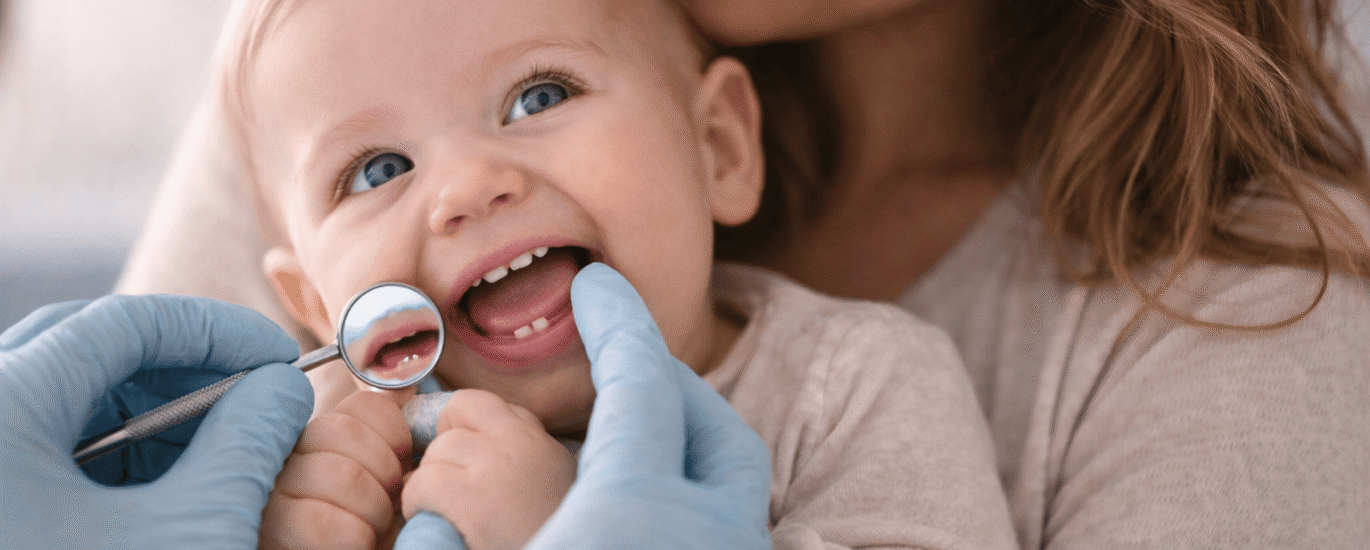
Teething is when the first set of teeth (milk teeth) erupt in your child’s mouth (oral cavity). It generally begins when your baby is around 6 months old. However, in some children, it can start as early as 3 months or as late as 12 months of age.
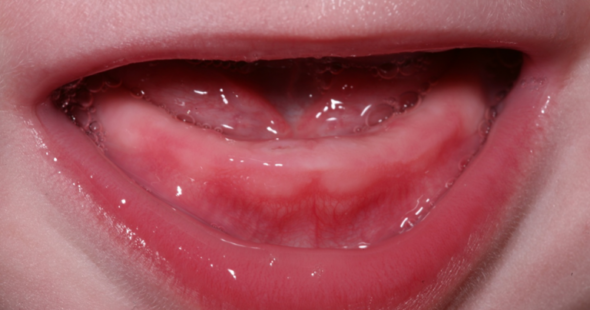
How do you know if your child is teething?
Your child might become irritated, cranky, and fussier than before because they feel swelling and sensitivity caused by an erupting tooth.
Red and swollen gums
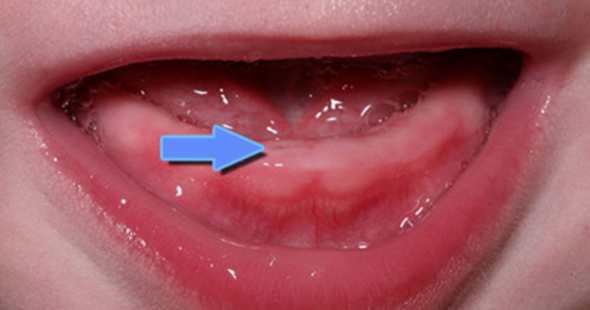
The child may show reluctance in eating.
Your baby might not be able to have sound sleep at night.
A very common behavior seen during teething is that your child keeps biting or sucking on whatever he or she gets.
Fever and diarrhoea may also be associated, but the correlation between fever, diarrhoea, and teething is not proven.
However, in many cases, teething occurs without any of these symptoms.
Causes of discomfort during teething
Development of teeth starts occurring when the baby is inside the mother’s womb (i.e., during the second trimester of pregnancy). Between 6 and 12 months after the child’s birth, milk teeth are ready for eruption. During eruption, the teeth tend to push through the gums, causing pressure on the gums.


